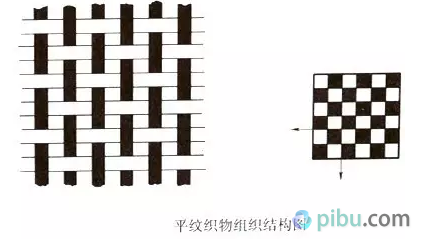
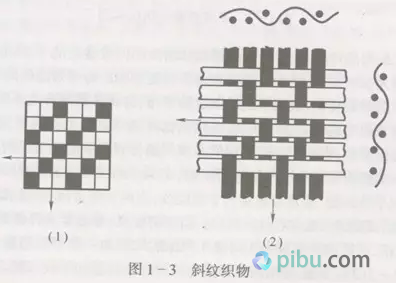
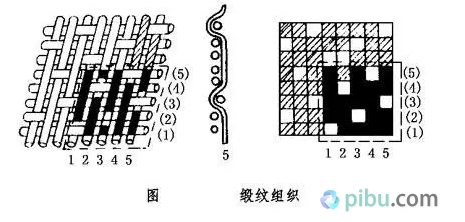
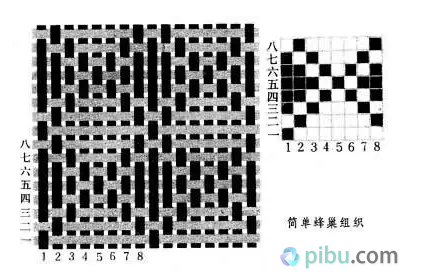
To say which woven fabric which strong? Amoy Web is professional. With years of working experience in woven fabrics, coupled with a professional Internet platform, you can easily send your fingers to the various woven fabrics. It may be that many textile “whites†have to ask. How do you judge the fabrics? So learn today. Woven fabric The yarns of the two systems (or directions) are perpendicular to each other, and the fabric formed by interweaving according to a certain rule is a woven fabric (also called a woven fabric). (Figure: The difference between the principle of weaving and knitting) The basic organization is the simplest and most basic organization among all kinds of organizations, and it is the basis for all kinds of changes and fancy organizations. The basic organization includes three organizations: plain, twill and satin. I. Plain weave Tissue Parameters Plain weave is the simplest of all fabrics. Its organizational rules are one up and two, and two alternates become a complete organization. Features:  The plain warp and weft yarns have the most interweaving points, and the yarns are more flexed. Therefore, the fabric has a flat cloth surface, a stiff body, a firm texture, and a compact appearance, but its handle is hard and its elasticity is small. In practical use, according to different requirements, various methods can be used, such as different thickness of warp and weft yarns, change of density of warp and weft yarns, and different combinations and configurations of twist, twist, and color, etc. Appearance effect. Plain weave is widely used in cotton, wool, silk and hemp fabrics, such as all kinds of plain flat cloth, fine texture of the spinning class, clear rhombus-shaped poplin, rosin with a pronounced uneven horizontal stripe appearance, and crepe. The effect of the seersucker and georgette, as well as the hidden effect of Veding, Paoli Division, tweed, flannel and so on. Two. Twill organization The characteristic of the twill weave is that the short warp or short warp is arranged in a stepwise manner, and a continuous slash is formed on the surface of the fabric. The organization of each warp yarn movement is the same, but the starting point is different. Features  The twill weave is divided by warp, weft and double-sided twill. Wherever the surface of the fabric is dominated by tissue points, for example, 2/1 is the surface twill, and vice versa, where 1/3 of the weft tissue points is the twill weft. The opposite side of the diagonal twill is the weft twill, but diagonally opposite. The proportions of the two types of tissue points on the positive and negative sides are the same, but they are diagonally opposite and are called double-sided twills. The slope of the diagonal lines is also different. In the twill weave, the angle α between the diagonal line and the horizontal line indicates the twill angle. As α increases, the larger the density, the steeper the straight line. The twill when α>450 is called an acute twill, and the diagonal twill when α<450 is a gentle twill, and when α=450, the fabric has the same latitude and longitude. The twill weave is less than the plain weave and has a long float. The fabric is softer and thicker than the plain weave, and the luster is also better. However, the fastness is not as good as that of the plain weave fabric. The diagonal lines on the surface of the twill weave can be clearly and distinctly selected according to the ratio of the twist direction to the warp and weft density. Or the lines are full, even and straight. Common twill fabrics have flat twills, khakis, khakis, and gabardines. Three. Satin weave The satin weave is the most complex tissue in the basic organization. Its characteristic is that there is only one single tissue point (organized or weft) on each warp (or weft), and two adjacent yarns There is a certain distance between the individual organization points, and it is covered by the long floating lines or latitude long lines on both sides, so that the surface of the fabric is almost entirely composed of a long floating line or long floating line, so the cloth surface is smooth and smooth. Good, soft texture. The common satin weave satin weave has a wide range of applications. In the cotton and wool fabrics, more than five satin weaves are used to obtain the tribute, the tribute, and the horizontal satin. In the silk fabrics, eight satin weaves are used to obtain a variety of luster, satin and flowers. Satin or satin fabric. IV. Change Organization Change organization is based on the original organization, and changes (such as changing the number of yarn cycles, floating length, flying number, diagonal line direction, etc.) and derived from the various derived organizations. Change organizations can be divided into three categories: plain weave change organizations (including heavy flat tissue, basket weave, etc.), diagonal twill changes (including enhanced twill, composite twill, angular twill, mountain twill, rhombus, twill, etc.), satin Change organization (including reinforcing satin, changing satin, etc.). Plain weave fabrics, some of the appearance of convex stripes effect, and more used to design poplin, linen, Rob, etc., while others are flat, soft and elastic feel, good luster, often used as a fabric, screen and other fabric edge organization. Twill-like changes in the appearance of tissue fabrics show a variety of twill effects, and some show a number of diagonal lines in parallel, and some yin and yang points, and some showed herringbone, Lu-like and so on. Therefore, it is widely used in cotton, wool, silk, chemical fiber and other fabric designs. The satin weave fabrics are more casual and free from design than the satin weave. Therefore, they have been widely used, such as in satin, satin, fabric and women's. application. V. Joint organizations and other complex organizations Joint organization . A new organization in which two or more organizations (former organizations or change organizations) are united by different methods, called joint organizations. The joint organization has special appearance effects on the surface. The common ones are the following: bar grid structure, through hole organization, mesh organization, rib structure, honeycomb structure, and caries tissue. These tissues are widely used in clothing and decorative fabrics. application. Complex organization , complex organization means that at least one of the warp and weft yarns consists of yarns of two or more groups of systems. This structure can increase the thickness of the fabric and the surface is dense, improve the abrasion resistance of the fabric and soft texture, or get some special properties. Depending on its organizational structure, it can be divided into several categories double weave, a double weave fluff tissue, tissue towels, leno weave and the like. They are widely used in autumn and winter clothing, decorative fabrics (bed blankets, upholstery) and industrial fabrics. Amoy cloth's main fabric is woven fabrics. If you have knitting requirements, Amoy Web will think for you too. There is an ad hoc buying area where you can post any purchases. As long as you register as a member of Amoy.com.com, you can publish your demand for free. Buyers with fabrics will see you for a quote. You only need to shop around and you can complete the purchase. Men'S Calf Socks,Football Socks,Calf Socks,Thick Socks Jiangsu Qianlima Stockings Co., Ltd , https://www.qlmsocks.com

For more content, please follow this site